SpringBoot在内部通过集成hibernate-validation,可以直接使用。项目中我们需要经常的去判断前端传递到后端的数据是否正确,这个时候需要些大量的if语句,代码相对比较中。这个时候validation就发挥了很大的作用。
Bean Validation 中内置的 验证规则:
| 注解 |
作用 |
| @Valid |
被注释的元素是一个对象,需要检查此对象的所有字段值 |
| @Null |
被注释的元素必须为 null |
| @NotNull |
被注释的元素必须不为 null |
| @AssertTrue |
被注释的元素必须为 true |
| @AssertFalse |
被注释的元素必须为 false |
| @Min(value) |
被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值 |
| @Max(value) |
被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值 |
| @DecimalMin(value) |
被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值 |
| @DecimalMax(value) |
被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值 |
| @Size(max, min) |
被注释的元素的大小必须在指定的范围内 |
| @Digits (integer, fraction) |
被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须在可接受的范围内 |
| @Past |
被注释的元素必须是一个过去的日期 |
| @Future |
被注释的元素必须是一个将来的日期 |
| @Pattern(value) |
被注释的元素必须符合指定的正则表达式 |
| |
|
Hibernate Validator 验证规则:
| 注解 |
作用 |
| @Email |
被注释的元素必须是电子邮箱地址 |
| @Length(min=, max=) |
被注释的字符串的大小必须在指定的范围内 |
| @NotEmpty |
被注释的字符串的必须非空 |
| @Range(min=, max=) |
被注释的元素必须在合适的范围内 |
| @NotBlank |
被注释的字符串的必须非空 |
| @URL(protocol=, host=, port=, regexp=, flags=) |
被注释的字符串必须是一个有效的url |
| @CreditCardNumber |
被注释的字符串必须通过Luhn校验算法, 银行卡,信用卡等号码一般都用Luhn 计算合法性 |
| @ScriptAssert (lang=, script=, alias=) |
要有Java Scripting API 即JSR 223 |
| |
|
| |
|
注意区分:
| 注解 |
作用 |
| @NotNull |
任何对象的value不能为null |
| @NotEmpty |
集合对象的元素不为0,即集合不为空,也可以用于字符串不为null |
| @NotBlank |
只能用于字符串不为null,并且字符串trim()以后length要大于0 |
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
其内置了:
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
1.请求方法中的请求参数上直接添加验证规则 如:@NotNull ,这里需要注意的是在该类上面需要添加@Validated。千万不要忘记,不然不会生效。
*@NotBlank @NotNull 如果在请求的方法上 直接使用 需要在该类上添加
* @Validated 注解 否则 该验证注解不生效
* 如果在请求对象中的属性上使用校验 注解 需要在方法请求参数中 该对象之前使用 @Validated 对象 对象名
public class UserController {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserController.class);
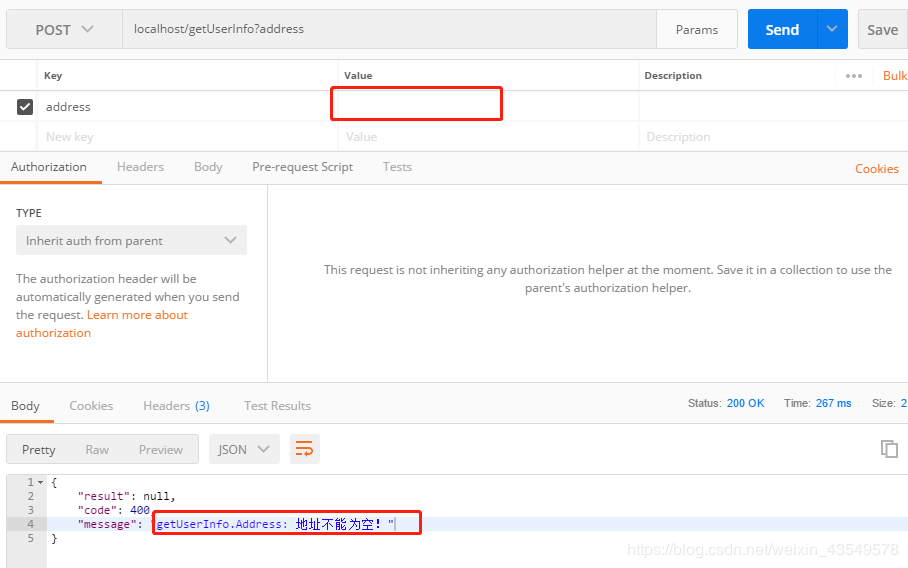
@RequestMapping("/getUserInfo")
public RestResultWrapper getUserInfo(@NotBlank(message = "地址不能为空!") @RequestParam(name = "address") String Address){
user.setAddress("ssssssss");
return new RestResultWrapper(user,0,"成功");
2.嵌套使用验证规则。如在实体类中的属性上使用验证规则。并且此时需要在请求实体类旁边添加@Validated
public class UserRequest {
@NotNull(message = "姓名不能为空")
//{user.name.notblank} 从 ValidationMessages.properties 获取到的
@NotNull(message = "{user.name.notblank}")
@Range(max = 150, min = 1, message = "年龄范围应该在1-150内。")
@NotNull(message = "编号不能为空")
@NotNull(message = "地址不能为空")
public class ValidateController {
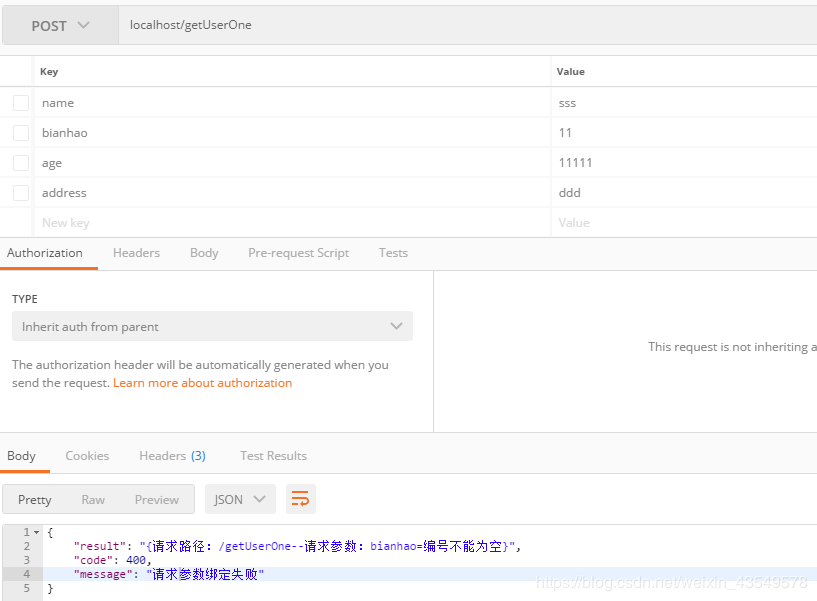
@RequestMapping("/getUserOne")
public RestResultWrapper getUserOne(@Validated UserRequest userRequest){
user.setAddress("ssssssss");
return new RestResultWrapper(user,0,"成功");
验证不通过的时候一般使用全局异常进行处理。设计到三个类:
ConstraintViolationException(方法参数校验异常)如实体类中的@Size注解配置和数据库中该字段的长度不统一等问题
MethodArgumentNotValidException(Bean 校验异常)
BindException (参数绑定异常)
请求时候不加任何参数:BindException
package com.springboot.validate.springbootvalidateexception.exception;
import com.springboot.validate.springbootvalidateexception.constant.RestResultWrapper;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import org.springframework.validation.BindException;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.validation.ObjectError;
import org.springframework.web.HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MissingServletRequestParameterException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.validation.ConstraintViolationException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class OnlineGlobalException {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(OnlineGlobalException.class);
@ExceptionHandler(ConstraintViolationException.class)
public RestResultWrapper handleValidationException(HttpServletRequest request, ConstraintViolationException ex) {
logger.error("异常:" + request.getRequestURI(), ex);
String collect = ex.getConstraintViolations().stream().filter(Objects::nonNull)
.map(cv -> cv == null ? "null" : cv.getPropertyPath() + ": " + cv.getMessage())
.collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
RestResultWrapper<String> restResultWrapper = new RestResultWrapper();
logger.info("请求参数异常",collect);
restResultWrapper.setCode(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value());
restResultWrapper.setMessage(ex.getMessage());
return restResultWrapper;
@ExceptionHandler(value = MethodArgumentNotValidException.class) //400
public RestResultWrapper methodArgumentValidationHandler(HttpServletRequest request, MethodArgumentNotValidException exception){
logger.info("异常:" + request.getRequestURI(), exception);
logger.info("请求参数错误!{}",getExceptionDetail(exception),"参数数据:"+showParams(request));
RestResultWrapper<String> restResultWrapper = new RestResultWrapper();
restResultWrapper.setCode(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value());
if (exception.getBindingResult() != null && !CollectionUtils.isEmpty(exception.getBindingResult().getAllErrors())) {
restResultWrapper.setMessage(exception.getBindingResult().getAllErrors().get(0).getDefaultMessage());
restResultWrapper.setMessage(exception.getMessage());
return restResultWrapper;
@ExceptionHandler(BindException.class)
public RestResultWrapper bindException(HttpServletRequest request, BindException pe) {
logger.error("异常:" + request.getRequestURI(), pe);
RestResultWrapper<String> restResultWrapper = new RestResultWrapper();
if(pe.getBindingResult()!=null){
List<ObjectError> allErrors = pe.getBindingResult().getAllErrors();
allErrors.stream().filter(Objects::nonNull).forEach(objectError -> {
map.put("请求路径:"+request.getRequestURI()+"--请求参数:"+(((FieldError) ((FieldError) allErrors.get(0))).getField().toString()),objectError.getDefaultMessage());
restResultWrapper.setCode(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value());
restResultWrapper.setMessage("请求参数绑定失败");
restResultWrapper.setResult(map.toString());
return restResultWrapper;
@ExceptionHandler(MissingServletRequestParameterException.class)
public RestResultWrapper missingServletRequestParameterException(HttpServletRequest request, MissingServletRequestParameterException pe) {
logger.error("异常:" + request.getRequestURI(), pe);
RestResultWrapper<String> restResultWrapper = new RestResultWrapper();
restResultWrapper.setCode(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value());
restResultWrapper.setMessage("该请求路径:"+request.getRequestURI()+"下的请求参数不全:"+pe.getMessage());
return restResultWrapper;
* HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException
@ExceptionHandler(HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException.class)
public RestResultWrapper httpRequestMethodNotSupportedException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException pe) {
logger.error("异常:" + request.getRequestURI(), pe);
RestResultWrapper<String> restResultWrapper = new RestResultWrapper();
restResultWrapper.setCode(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value());
restResultWrapper.setMessage("请求方式不正确");
return restResultWrapper;
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public RestResultWrapper otherException(HttpServletRequest request, Exception pe) {
logger.error("异常:" + request.getRequestURI(), pe);
RestResultWrapper<String> restResultWrapper = new RestResultWrapper();
restResultWrapper.setCode(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value());
restResultWrapper.setMessage(getExceptionDetail(pe));
return restResultWrapper;
private String getExceptionDetail(Exception e) {
StringBuilder stringBuffer = new StringBuilder(e.toString() + "\n");
StackTraceElement[] messages = e.getStackTrace();
Arrays.stream(messages).filter(Objects::nonNull).forEach(stackTraceElement -> {
stringBuffer.append(stackTraceElement.toString() + "\n");
return stringBuffer.toString();
public String showParams(HttpServletRequest request) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>();
StringBuilder stringBuilder=new StringBuilder();
Enumeration paramNames = request.getParameterNames();
stringBuilder.append("----------------参数开始-------------------");
stringBuilder.append(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
if(Objects.nonNull(paramNames)){
while (paramNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String paramName = (String) paramNames.nextElement();
String[] paramValues = request.getParameterValues(paramName);
if (paramValues.length >0) {
String paramValue = paramValues[0];
if (paramValue.length() != 0) {
stringBuilder.append("参数名:").append(paramName).append("参数值:").append(paramValue);
stringBuilder.append("----------------参数结束-------------------");
return stringBuilder.toString();
验证请求参数还可以通过自定义注解:
如:
手机号码:
@ConstraintComposition(CompositionType.OR)
@Pattern(regexp = "1[3|4|5|7|8|6][0-9]\\d{8}")
@Length(min = 0, max = 16)
@Constraint(validatedBy = {})
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.PARAMETER })
public @interface PhoneVerification {
String message() default "手机号校验错误";
Class<?>[] groups() default {};
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default {};
身份证:
@Target( { METHOD, FIELD, ANNOTATION_TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Constraint(validatedBy = CardValidate.Validator.class)
public @interface CardValidate {
String message() default "invalid phone number";
Class<?>[] groups() default {};
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default {};
class Validator implements ConstraintValidator<CardValidate, String> {
public boolean isValid(String carid, ConstraintValidatorContext arg1){
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(carid)){
//RegexValidateUtils.checkCard(carid)
分组校验:https://www.cnkirito.moe/spring-validation/
@Validated和@Valid区别:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27680317/article/details/79970590
@Validated和@Valid在嵌套验证功能上的区别:
@Validated:用在方法入参上无法单独提供嵌套验证功能。不能用在成员属性(字段)上,也无法提示框架进行嵌套验证。能配合嵌套验证注解@Valid进行嵌套验证。
@Valid:用在方法入参上无法单独提供嵌套验证功能。能够用在成员属性(字段)上,提示验证框架进行嵌套验证。能配合嵌套验证注解@Valid进行嵌套验证。
代码参考:https://github.com/timeday/springboot-validateexception

